Vol.24 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(4) "SHEAR OPTIONS"
This time, we will introduce “Shear Angle” from the questions we have contacted the Tool Consultation.
SHEAR OPTIONS ON PUNCH
please tell us the type and selection criteria of the shear angle.
The shear angle is obtained by processing the punch edge surface into a “convex” or “concave” shape, and is effective in
- 1.Reduce tonnage
- 2.Slug pulling
- 3.Reduce noise
Popular shear shapes are bellows.
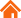
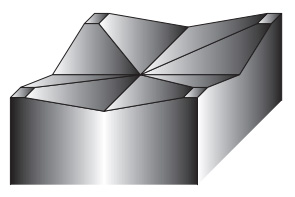
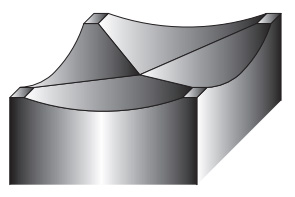
Fig.1 Type of shear angle
Roof top shear
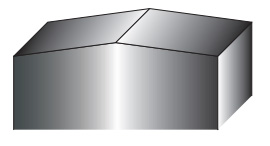
Concave shear
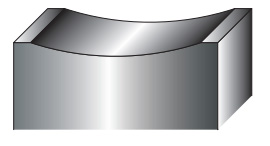
Inverted shear
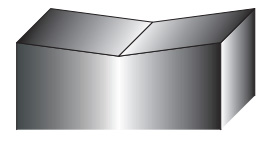
4way inverted
4way concave
SHEAR ANGLE TYPES AND SELECTION CRITERIA
ROOF TOP SHEAR
- 1.The most common shear angle.
- 2.At Conic, shear angles are standard at 2 degree and 5 degree.
- 3.It is relatively easy for customers to perform regrinding.
Fig.2 Resistant direction to the punch tip
In case of roof top shear
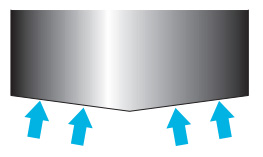
In case of concave shear

CONCAVE SHEAR, INVERTED SHEAR
- 1.This shear angle is suitable for slitting processing.
-
2.Since force is applied outward to the cutting edge during punching (See Fig. 2),
when processing a thick plate with a narrow punch, cracks may occur from the bottom.
In the case of urethane kicker, it may be damaged early. - 3.It is difficult for customers to regrind without dedicated jigs.
4 WAY CONCAVE SHEAR, 4 WAY INVERTED SHEAR
- 1.This shear angle is suitable for slitting with a square shape in both X and Y directions.
FLAT (NO SHEAR)
-
1.In general, small diameter punches do not have a shear angle because the removal load is small.
However, when processing thick plates,
it may be added as a measure to prevent slug pilling. - 2.There is no shear angle for the blank type (if the slug is a product) because the blank is deformed.
ADVICE ON ONE POINT:Calculating formula of tonnage with shear
Tonnage with shear = tonnage without shear x shear coefficient
-
■When the material thickness is thinner than the shear angle height.
Shear angle coefficient = 0.5 - ■When the material thickness is thicker than the shear angle height.
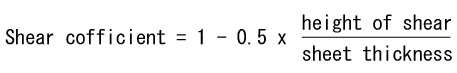
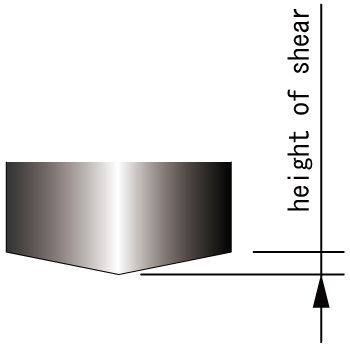
- ※For calculation of tonnage without shear angle, refer to Technical Information Vol.13
“Calculation formula frequently used in sheet metal”.
-
vol.1 COUNTERMEASURES FOR SLUG PULLING IN PUNCHING PROCESS
-
vol.2 LIFE COUNTERMEASURE FOR TOOLING
-
Vol.3 TOOL MAINTENANCE
-
Vol.4 FORMING TOOL
-
Vol.5 MATERIAL FOR TOOLING
-
Vol.6 FOR CLEARANCE OF THE CUTTING DIE
-
Vol.7 ABOUT TURRET PUNCH PRESS MACHINE
-
Vol.8 VARIOUS KINDS OF SPECIAL SHAPE
-
Vol.9 PARTS NAME OF STANDARD TOOLING
-
Vol.10 EACH NAMES OF FORMING TOOL
-
Vol.11 MATERIAL PROPERTIES (STEEL)
-
Vol.12 MATERIAL PROPERTIES
-
Vol.13 CALCULATION FORMULAS FREQUENTLY USED IN SHEET METAL
-
Vol.14 HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT FREE TOOL
-
Vol.15 HOW TO DRAW AND READ DRAWINGS
-
Vol.16 HOW TO DRAW AND READ DRAWING (PRACTICAL USE)
-
Vol.17 SHAPE INSTRUCTION FOR FORMING TOOLS(1)
-
Vol.18 SHAPE INSTRUCTION FOR FORMING TOOLS(2)
-
Vol.19 CODE MANAGEMENT
-
Vol.20 BENDING TECHNICAL INFORMATION
-
Vol.21 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(1) "COUNTERMEASURES FOR GALLING"
-
Vol.22 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(2) "BURRING FOR THREAD FORM"
-
Vol.23 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(3) "PITCH OF SINGLE PIERCING"
-
Vol.24 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(4) "SHEAR OPTIONS"
-
Vol.25 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(5) "HOLDING MARK"
-
Vol.26 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(6) "SOLUTION FOR SLUG PULLING OF A SHEET METAL WITH PROTECTIVE FILM"
-
Vol.27 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(7) "MATERIAL WARPING PREVENTION DURING"
-
Vol.28 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(8) "WARPING PREVENTION OF BLANKING OUT"
-
Vol.29 TECHNICAL COUNSELING FAQ(9) "COUNTERSINK FOR COUNTERSUNK SCREW"
-
Vol.30 THE ORDERING GUIDE(1) "HOW TO INSTRUCT SHAPE AND DIMENSIONS"
-
Vol.31 THE ORDERING GUIDE(2) "REFERENCE KEY DIRECTION"
-
Vol.32 THE ORDERING GUIDE(3) "ANGLE INDICATION OF ANGLED TOOL"
-
Vol.33 THE ORDERING GUIDE(4) "SELECT SPECIFICATION OF PUNCH"
-
Vol.34 THE ORDERING GUIDE(5) "DIE SPECIFICATION SELECTION"