Vol.15 Cara menggambar dan membaca gambar (Dasar)
When working on machining, you always have to use the drawings.
Proper viewing and drawing of drawings is important for conveying information accurately.
This time, we summarized how to draw and read the drawings.
DESCRIPTION AND NAMES OF THE DRAWING LINES
◆ There are the following four types of lines depending on the shape.
| Solid Line |

|
Continuous line |
| Dotted line |

|
The line where a short line is repeated in turn |
| Chain line |

|
The line where a line of the length of two kinds of length is repeated in turn |
| Chain double-dashed line |

|
The line where a line of the length of two kinds of length is repeated in turn, such as long, short, short, long, short, short |
◆ There are 3 kinds of line thickness.
| Thin line |

|
| Thick line |

|
| Extra thick line |

|
The ratio of the thickness of the thin line, thick line, and extra-thick line is 1: 2: 4.
THE USERS OF LINE
Use different types of lines depending on the purpose.
The main uses according to the type of line are as follows.
| Line description | Name by use | The Uses of Line | |
| Thick solid line |

|
Outline | It is used for represent the shape of the visible part of the object. |
| Thin solid line |

|
Dimension line Extension line Leader line |
It is used for writing dimensions. It is used to draw from a figure to fill in dimensions. It is used for drawing out descriptions and symbols. |
| Thin dashed line |

|
Hidden outline | It is used for represent the shape of the invisible part of the object. |
| Thick dashed line |

|
||
| Thin chain line |
|
Center line Reference line Pitch line |
It is used for represent the center of the figure. In particular, it is used to clearly indicate the basis of position determination. A reference line that takes the pitch of repeated figures. |
| Thin Chain doubledashed line |

|
Imaginary line | It is used to display information that is not actually there for reference. |
| Thin wave line |

|
Break line | A line representing the boundary when a part of an object is temporarily removed. |
| Thin chain line with the part which changes of direction |
|
Cutting line | When drawing a sectional view, it is used to show the cutting position in the corresponding figure. |
| Thin solid line with Draw regularly |
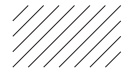
|
Hatching | It is used to distinguish a specific part of a figure from other parts. For example, the cut end of a sectional view is shown. |
TRIGONOMETRY
In general, mechanical drawings are drawn by trigonometry.
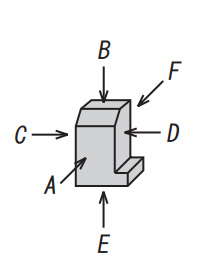
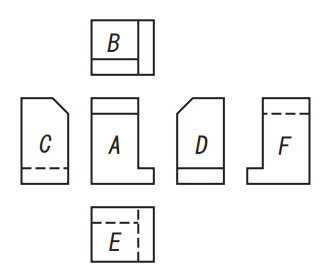
Correct placement drawn with trigonometry
- A :Front view
- B :Plan view
- C :Left-side view
- D :Right-side view
- E :Bottom view
- F :Back side view
SYMBOL FOR DIMENSIONING USED IN DRAWING
In drafting, use a dimension symbol to clarify the meaning of the dimension by adding it to the numerical value representing the dimension.
The main dimension auxiliary symbols are as follows.
| Description of numetrical value | Symbol | Purpose of use |
| Diameter |
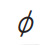
|
Put it before diameter dimension |
| Radius |

|
Put it before radius dimension |
| Diameter of Sphere |
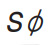
|
Put it before diameter of sphere dimension |
| Radius of Sphere |

|
Put it before radius of sphere dimension |
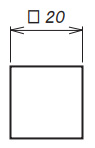
| Sides of Square |

|
Put it before dimension of a side of square |
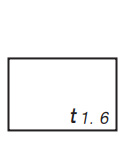
| Thickness of material |
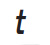
|
Put it before thickness of material dimension |
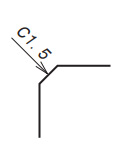
| 45 degs chamfering |
|
Put it before 45 degs chamfering dimension |
Example of use
| Diameter | Radius | Diameter of Sphere | Radius of Sphere | Sides of Square | Thickness of materia | 45 degs chamfering |
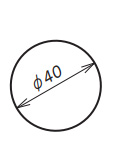
|
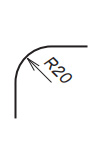
|
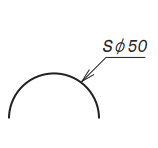
|
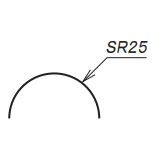
|
|
|
|
| Diameter | Radius |

|

|
| Diameter of Sphere | Radius of Sphere |

|

|
| Sides of Square | Thickness of materia |

|

|
| 45 degs chamfering |

|
Vol.1 Solusi untuk mencegah slug naik kepermukaan
Vol.2 Solusi untuk meningkatkan masa pakai tool
Vol.3 Pemeliharaan tool
Vol.4 Forming tool
Vol.5 Material yang digunakan untuk memproduksi tool
Vol.6 Die Clearance
Vol.7 Mesin Turret Punch Press
Vol.8 Berbagai macam Bentuk spesial
Vol.9 Nama bagian-bagian tool standar
Vol.10 Forming tool
Vol.11 Jenis material (Baja)
Vol.12 Jenis material (Logam nonferrous)
Vol.13 Rumus penghitungan yang populer digunakan dalam Lembaran logam
Vol.14 Tool bebas pengaturan ketinggian
Vol.15 Cara menggambar dan membaca gambar (Dasar)
Vol.16 Cara menggambar dan membaca gambar (Penggunaan praktis)
Vol.17 Instruksi bentuk untuk forming tools(1)
Vol.18 Instruksi bentuk untuk forming tools(2)
Vol.19 Manajemen kode
Vol.20 Informasi teknis bending
Vol.21 T&J konseling teknis(1) "COUNTERMEASURES FOR GALLING"
Vol.22 T&J konseling teknis(2) "BURRING FOR THREAD FORM"
Vol.23 T&J konseling teknis(3) "PITCH OF SINGLE PIERCING"
Vol.24 T&J konseling teknis(4) "SHEAR OPTIONS"
Vol.25 T&J konseling teknis(5) "HOLDING MARK"
Vol.26 T&J konseling teknis(6) "SOLUTION FOR SLUG PULLING OF A SHEET METAL WITH PROTECTIVE FILM"
Vol.27 T&J konseling teknis(7) "MATERIAL WARPING PREVENTION DURING"
Vol.28 T&J konseling teknis(8) "WARPING PREVENTION OF BLANKING OUT"
Vol.29 T&J konseling teknis(9) "COUNTERSINK FOR COUNTERSUNK SCREW"
Vol.30 Panduan pemesanan(1) "HOW TO INSTRUCT SHAPE AND DIMENSIONS"
Vol.31 Panduan pemesanan(2) "REFERENCE KEY DIRECTION"
Vol.32 Panduan pemesanan(3) "ANGLE INDICATION OF ANGLED TOOL"
Vol.33 Panduan pemesanan(4) "SELECT SPECIFICATION OF PUNCH"
Vol.34 Panduan pemesanan(5) "DIE SPECIFICATION SELECTION"